Nino just posted this brilliant article on Cinema5D following Philip Bloom's A7S workshop and B&H, focusing on key settings to properly set up the camera for video! Definitely worth a read, thanks for the share.
Welcome to the boardroom
I'm doing a few productions for the IABM in the lead up to their annual conference in December, which included a video shoot in London at IBM; a panel discussion on the key topics of the conference, and the industry at the moment.
John Ive, the director of business and technology at the IABM chaired the discussion, with six of the top decision makers in the industry around the table, which included: Dominic Stone (Our host at IBM and multimedia executive), Rob Roberts (Avid), Marc Risby (Boxer), David Peto (Aframe), Chris Steele (Marquis), Paul Glasgow (Chyron Hego).
It was an early start for myself and Glen, to get a head start in the traffic heading up to the South Bank. Usually I would get the train, but as this was a full setup I required my little cars assistance to get the equipment there!
Glen at IBM
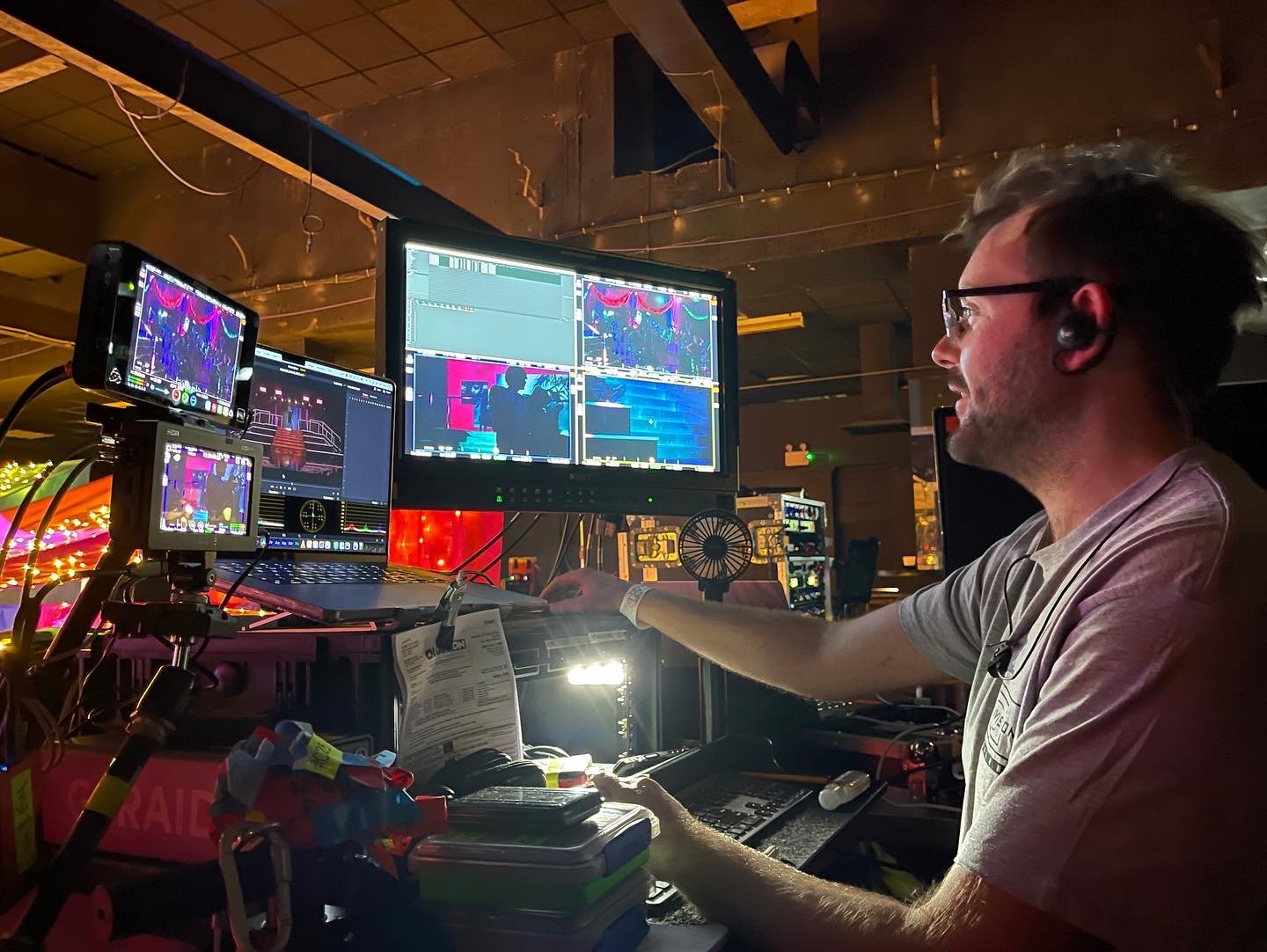
Me at IBM!
We arrived at the IBM office on the South Bank with plenty of time to spare, and after unloading the equipment in the loading bay we parked up in the National Theater and met our host for the day, Dominic. A wonderful chap with a wealth of experience as a television producer, many thanks for your hospitality throughout the day!
Trolley fulla gear!
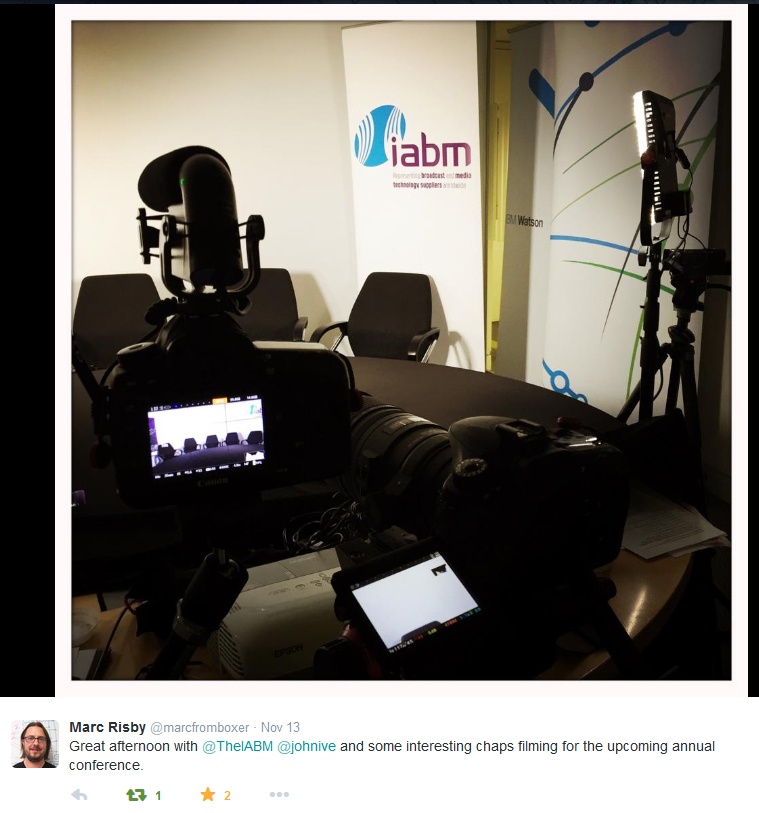
What the conference room at IBM looked like before we got our hands on it!
Once we had access to the conference room, we began the setup and moved any unnecessary furniture out of the way. Manfrotto has greatly helped me on this as much of the kit is new and definitely new to this kind of video environment too, and after IBC I was very keen to try out the new tripods; which now can be lowered to almost ground level with innovative locking joints. Also, although I'm using a 5D and telephoto lenses to shoot with (so the load is not very heavy), but having steady and smooth shots are imperative to keeping a good composition, both the tripod and video head allow me to achieve shake free pans and tilts, which can be counter balanced depending on your camera, lens and accessory setup.
The new light stands are awesome. I know it is something simple, but it makes a massive difference. Stands and poles can often get mislaid, damaged in transit or in use, or simply can't withhold a wide variety of lights and accessories. These on the other hand have a brilliant locking system to hold multiple stands together, meaning they can be carried and transported very easily. They are not heavy, and can take a heavy load (not that these SPECTRA 1X1 LED panels are that heavy)!
Panel video setup with Manfrotto 1x1 bi-colour LED light
After lunch, we checked the colour temperature on the four lights; the two front facing the panel, one giving a back light onto the speakers and background, and a smaller 900 panel to push a little extra light into the right panelists. All of the lights are bi-colour, which gives maximum flexibility when the video scenario changes so frequently.
The lights I used were: Manfrotto Spectra 1x1FT x 3, Spectra 900FT and the 1004BAC pro light stands.
To make sure all of the cameras were exposed and set correctly, we did a custom white balance and orientated around the cameras and lights to make sure we achieved the best out of the setup.
I transported the camera and audio equipment in the Manfrotto Pro Backpack50 as its large capacity was required for the amount of kit I needed which included:
- Canon 5D mkIII
- Canon 60D
- Tamron 24-70
- Sigma 70-200
- Samyang 35mm
- Samyang 14mm
- Zoom H1
- Zoom H6
- Sennheizer ENG-G3
- Rode Lavalier
- Roto-mic
- Canon batteries, AA batteries for microphones and audio recorders, chargers for all.
I also had the Manfrotto 536 MPRO tripod and 504 HD video head in the large tripod bag, and the ProCX-3 and Pro-B for the other cameras.
Marc Risby, one of the panelists tweets about his experience!
While we were setting up!
Shortly after our panelists arrived, and they were eager to get started in discussion; I put the lapel mics on and plugged them into the H6. John kindly allowed us to use a couple of cameras and microphones for the extensive number of panelists. The Sony ECM-77 are great lav mics with good audible response, as is the Rode Lavalier which I used with the MiCon-1 connector into the ENG-G3 wireless kit.
I got the panel talking for a practice run through while I checked the audio levels on the H6, which was placed under John's chair (due to the cable length I could not monitor the camera from my filming position).
If you've been following me on Twitter, you'll have seen I have been looking for a wide angle lens for both an APS-C and FF sensor (so far Canon's 16-35 F/2.8 is best), so I was without my Tamron 17-50mm (my standard lens on the 60D as a wide). To compensate for this, I alternated my usual video setup from 5D and Sigma 70-200mm for an MCU and 60D and 17-50mm for a wide to; 5D and Tamron 24-70mm for a wide and 60D and 70-200mm for an MCU which allowed me to capture a good wide angle of the whole panel, as well as a great MCU on the speaker.
The 504HD video head has integrated fluid drag and resistance which makes panning and tilting a dream for video; it is smooth, yet easily changed depending on the subject and timing of the camera moves. A large pan-handle makes the motion firm and steady throughout.
With a vast experience in broadcasting from all of the panelists, it was difficult not to get distracted into the conversation. After each discussion we shot some VoxPops for the conference with the other panelists that did not participate in that panel, which will be used throughout the presentations and panels at the IABM annual conference in December.
Unlike the Zoom H4N, the H6 has an incredible power consumption rate meaning on four AA batteries it can record multiple channels (four in this care) for a good 2 hours without needing to change! This meant I could rely on it recording stand-alone under Johns seat without monitoring, after each channel was correctly set (with a general limiter on).
In terms of the camera settings I was using:
- VisionTech2 Picture Profile
- F/4.5 on the MCU so focusing between panelists was minimum
- Because of light setting, as well as not much fast motion happening I reduced the electronic shutter to 1/33.
- ISO between 400 and 640 due to the good light produced from the 1x1's!
Once the filming was complete, we quickly de-rigged the setup so we could get out of London as quickly as possible; not to get held up with traffic queues etc.. Thankfully, all of the Manfrotto gear we had is fast to setup and tear down so we were ready to leave within half an hour or so!
Once I got back home, I begun the ingest and backup process; remembering to have 3 copies of the footage and audio on separate drives in case any fail. I also began re-naming the files so it is easier for me to locate specific panelists microphones when doing the audio mix-down.
Although the Zoom H6 is an awesome recorder, it for some reason records track 3 and 4 together (as a stereo channel) so I had to split the Tr3-4 into separate Track 3 and Track 4 files using Audition. This is a simple process, but I wonder if this can be changed in the device itself?
Here you can see the top track is different to the other, this is because the T3 and T4 inputs were from different speaker microphones, but recorded together. To resolve this, I simply solo'd the track I needed, selected ALL and copied, created a new audio stereo track and pasted the track there; this creates a Left or Right track for you in the new audio file.
Here, I've created a new stereo audio track and pasted the solo'd track into it. The new stereo audio file then replicated the audio on both tracks. I then saved this as a new audio track.
In Pluraleyes, I created the four camera sources and imported their respective video files, and then singularly imported each audio track into a new audio recorder as a new audio source (instead of importing the five tracks into the same audio recorder). This would allow me to control not only each track individually, but also when I separate the four sections into their own multi-camera sequences I have separate audio tracks rather than one reallyyy long one.
You can see here that the audio tracks from each microphone are separated in the sync.
I was amazed at the speed of the sync, only 1 minute 8 seconds to sync all of the video and audio from many different sources! I then exported the sync as both an XML and XML with replaced audio from Pluraleyes, and created a new Premiere Pro project for this production.
I imported the XML file into the new project, which imports and creates a new sequence with the synced footage in place. So easy! I then placed the footage into their respective sequences depending on the discussion topic, and prepared them for multi-camera editing!
The sequences are now ready to be cut using the Multi-camera interface! Unfortunately I can't show anymore as this is an IABM member exclusive video, but I hope you have enjoyed seeing how videos like this are produced on a small scale!
Video Questions; Choosing the right camera, picture profiles and using ND filters!
Heyo all! Thanks for sending in your questions, I will try to answer as many as I can will practical, real world examples! If you have any more, please send them my way! Question from Chris via Facebook: "Can you recommend any camcorders for HD video and good low light performance?"
Answer: A DSLR for video is not the right choice everytime. Why do you think television broadcasters use camcorders and system cameras? For broadcasting, there are regulations and legal limits that must be followed for the final video to be shown live; there are many including the compression of the video signal, the black and white level (check out waveform monitors and video signal) to name a couple. DSLR's do not adhere to these regulations hence we don't see TV crews running around with 5D's in London.
Where DSLR's produce a great image due to the large CMOS sensor, they have big restrictions such as needing to change lenses, poor audio support (unless you invest in audio equipment), rolling shutting, aliasing, moire.. I could keep going.
So, taking camcorders in the equation; most have long zoom ranges (20x and more!) at wide apertures, with additional digital gain, in built ND filters, built in stereo microphone and audio in/out. The sensors are different too, some using CCD (which splits the 3 colour channels) for better colour rendition and less compression.
These days, manufacturers such as Sony, Canon, JVC produce ENG (electronic news gathering) camcorders with those above features, meaning no extra kit to carry, most are hand held or shoulder mount for ease of use. Therefore it is seemingly easier to video on a camcorder, until you require a large sensor camera for artistic video.
Product recommendations for camcorders - Sony AX and VG range, Canon Legria, XA and XF range, JVC produce great camcorders too and have stepped up their game over the last year with the GM-HY range including a 4K model too.
If you want to spend a little more, the Sony HXr-NX3 (recently reviewed by Den Lennie) looks incredible for what you get in one camera - http://www.sony.co.uk/pro/article/broadcast-products-get-close-up-hxr-nx3
Next question from SAHIB on Twitter: "Do you use a neutral picture style when shooting, and do you use neutral density filters?"
Answer: For those unaware of picture profiles on your camera, check them out in the 3rd section of the movie shooting (red) menu (for Canon users). There are a number of options listed, which alter the way the picture is recorded depending on your choice, you can also customize these profiles too using the INFO button.
Canon picture styles - Standard, Portrait, Landscape, Neutral, Faithful, Monochrome.
I will not be detailing the ins and outs of all the picture styles, more of a visual comparison.
What does a picture profile do? Much like LUTS, picture styles adjust the intensity level of the; Sharpness, Contrast, Saturation and Colour Tone in the image, so what picture profile you use can change the 'look' of the video you capture.
Check out this video I put together today showing the results of the cameras picture profiles, and others I have loaded onto the camera. You can see a clear change in the image, but it is subtle differences that will make your video work stand out.
I previously used the Neutral picture profile, customized to reduce the contrast, saturation and colour tone to produce a very grey and flat image. I was using this profile to achieve this look, as it is how RAW footage is captured to then be graded in post production. Neutral does replicate this 'flat' look, but after doing research into other profiles, Neutral reduces the data that is required in the picture (the contrast and saturation) that I would then put back in in post. This causes noise to be generated in the image, and can cause it to look unnatural and crushed, as the contrast and saturation that had been removed by the picture profile is being added back in later in the workflow.
That was long, but I hope it makes sense. If you compare the 'Standard' to 'Neutral' there is an evident drop in saturation and contrast, with a loss of detail in the top of the trees. If you compare 'Neutral' to 'VisionColor', there is an increase in saturation and contrast in the shadows and highlights.
The 'Neutral' picture style, similar to Technicolor CineStyle reduces the data the sensor captures, so I would not recommend using it if you plan to do colour correction and grading in your workflow. REMEMBER - whatever you capture when out filming will 'burn in' the detail, colours, sharpness and contrast into the image, making it harder to edit and remove unwanted errors. So, it would be better to use a profile that holds the data and detail so if wanted, you could work on grading the footage later.
From tests and experimenting, I favor the VisionColor profile; it is not as destructive as Neutral, holding colour and contrast without making the image flat. I definitely recommend checking them out here.
Next Question from SAHIB on Twitter: "Can ND filters change the style of video?"
Answer: This does depend on what and where your video shoot is. If you are working indoors, or with lighting that can be controlled by you then neutral density filters may not be required as you can alter the brightness of the scene by reducing the intensity of the lights. However, if you're out filming in a situation where you have little to no control over the lighting, then ND filters are key.
Personally I use variable ND filters, currently from Polaroid but much better filters are available from Hoya & Tiffen. The function of these filters is to reduce the light entering the lens, meaning camera settings can be kept the same. This allows you to follow the 180 degree shutter rule, which means keeping your electronic shutter speed at 1/50th to reproduce film-like and realistic motion blur.
So, with your shutter speed locked at 1/50, and your chosen aperture has been set, the only other exposure altering options you have is to ride the camera ISO to make the image brighter or darker.
PROBLEM!
With a fast aperture of F/2.8, and you are currently shooting in sunny daylight, your image is going to be very over exposed. Reducing the aperture to F/8 or F/11 may correctly expose the image but you have lost your depth of field! What to do!
Get some Variable ND Filters!
These ND filters rotate, allowing a variable ND amount to be set externally, without changing your cameras settings! This means that you can keep your cinematic depth of field and realistic motion blur without reducing the shutter speed to 1/250th or your aperture to F/11.
I recently shot this video using an ND filter on an 85mm T/1.5, which allowed me to shoot continually at T/1.5 for extreme shallow depth of field.
Making a quick edit: Variable ND filters are one of many options. ND Filters also come in stops; increasing by a factor of doubling so 2, 4, 8 etc. If you can stretch to separate stop ND filters they work just as well, and with the lower end (under £100 products) they will be better quality than one under £100.
In videography and cinematography, ND filters are applied in the matte box in front of the lens. So if you plan to use one, look in to matte boxes with the ability to add filters, but prepare to pay for it!
Well, that covers Video Questions for today! I hope to have answered and covered all bases, and remember they are from my personal knowledge and experience.
Got any more? Send them my way!