Heyo all! Thanks for sending in your questions, I will try to answer as many as I can will practical, real world examples! If you have any more, please send them my way!
Question from Chris via Facebook: "Can you recommend any camcorders for HD video and good low light performance?"
Answer: A DSLR for video is not the right choice everytime. Why do you think television broadcasters use camcorders and system cameras? For broadcasting, there are regulations and legal limits that must be followed for the final video to be shown live; there are many including the compression of the video signal, the black and white level (check out waveform monitors and video signal) to name a couple. DSLR's do not adhere to these regulations hence we don't see TV crews running around with 5D's in London.
Where DSLR's produce a great image due to the large CMOS sensor, they have big restrictions such as needing to change lenses, poor audio support (unless you invest in audio equipment), rolling shutting, aliasing, moire.. I could keep going.
So, taking camcorders in the equation; most have long zoom ranges (20x and more!) at wide apertures, with additional digital gain, in built ND filters, built in stereo microphone and audio in/out. The sensors are different too, some using CCD (which splits the 3 colour channels) for better colour rendition and less compression.
These days, manufacturers such as Sony, Canon, JVC produce ENG (electronic news gathering) camcorders with those above features, meaning no extra kit to carry, most are hand held or shoulder mount for ease of use. Therefore it is seemingly easier to video on a camcorder, until you require a large sensor camera for artistic video.
Product recommendations for camcorders - Sony AX and VG range, Canon Legria, XA and XF range, JVC produce great camcorders too and have stepped up their game over the last year with the GM-HY range including a 4K model too.
If you want to spend a little more, the Sony HXr-NX3 (recently reviewed by Den Lennie) looks incredible for what you get in one camera - http://www.sony.co.uk/pro/article/broadcast-products-get-close-up-hxr-nx3
Next question from SAHIB on Twitter: "Do you use a neutral picture style when shooting, and do you use neutral density filters?"
Answer: For those unaware of picture profiles on your camera, check them out in the 3rd section of the movie shooting (red) menu (for Canon users). There are a number of options listed, which alter the way the picture is recorded depending on your choice, you can also customize these profiles too using the INFO button.
Canon picture styles - Standard, Portrait, Landscape, Neutral, Faithful, Monochrome.
I will not be detailing the ins and outs of all the picture styles, more of a visual comparison.
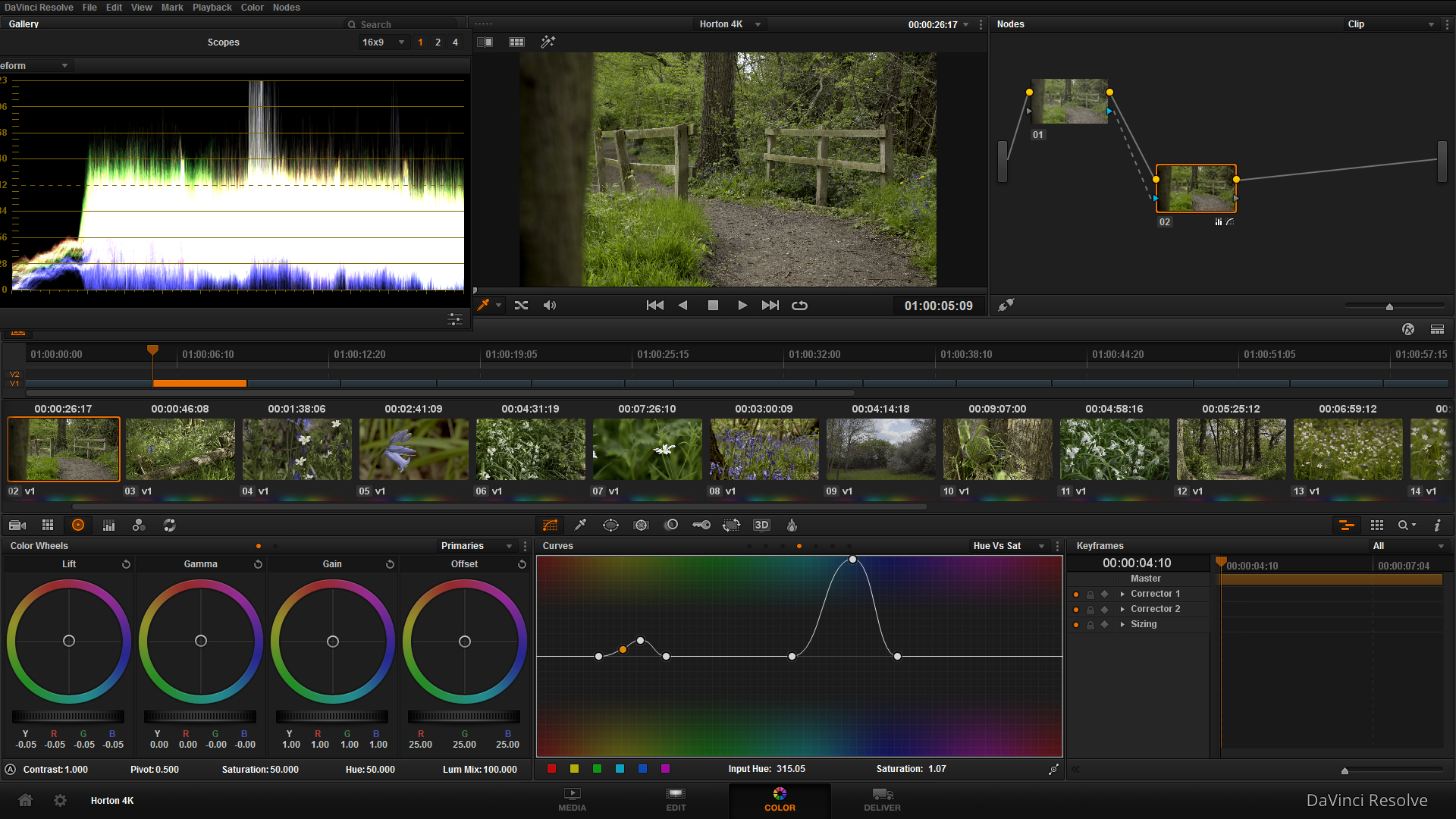
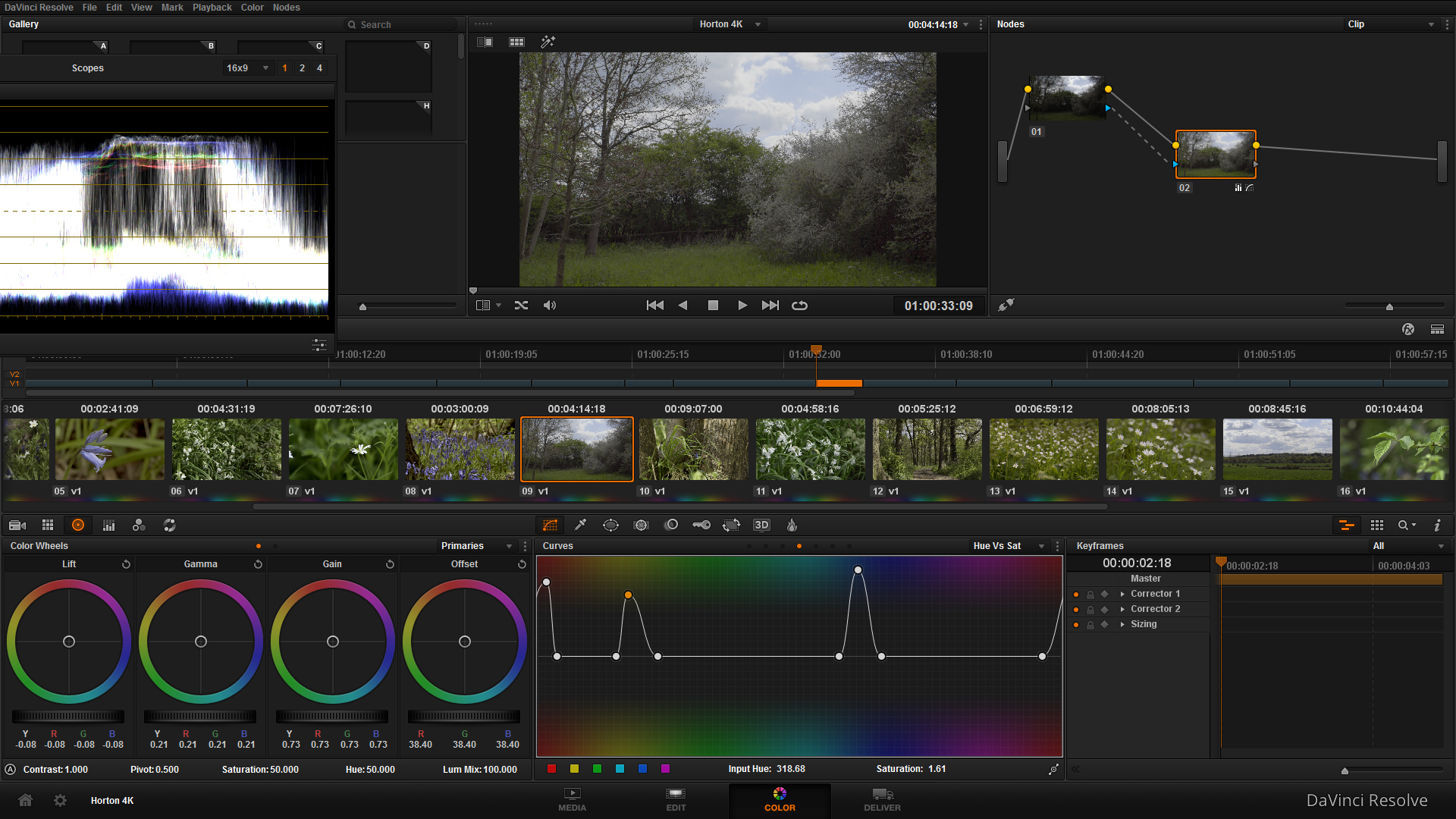
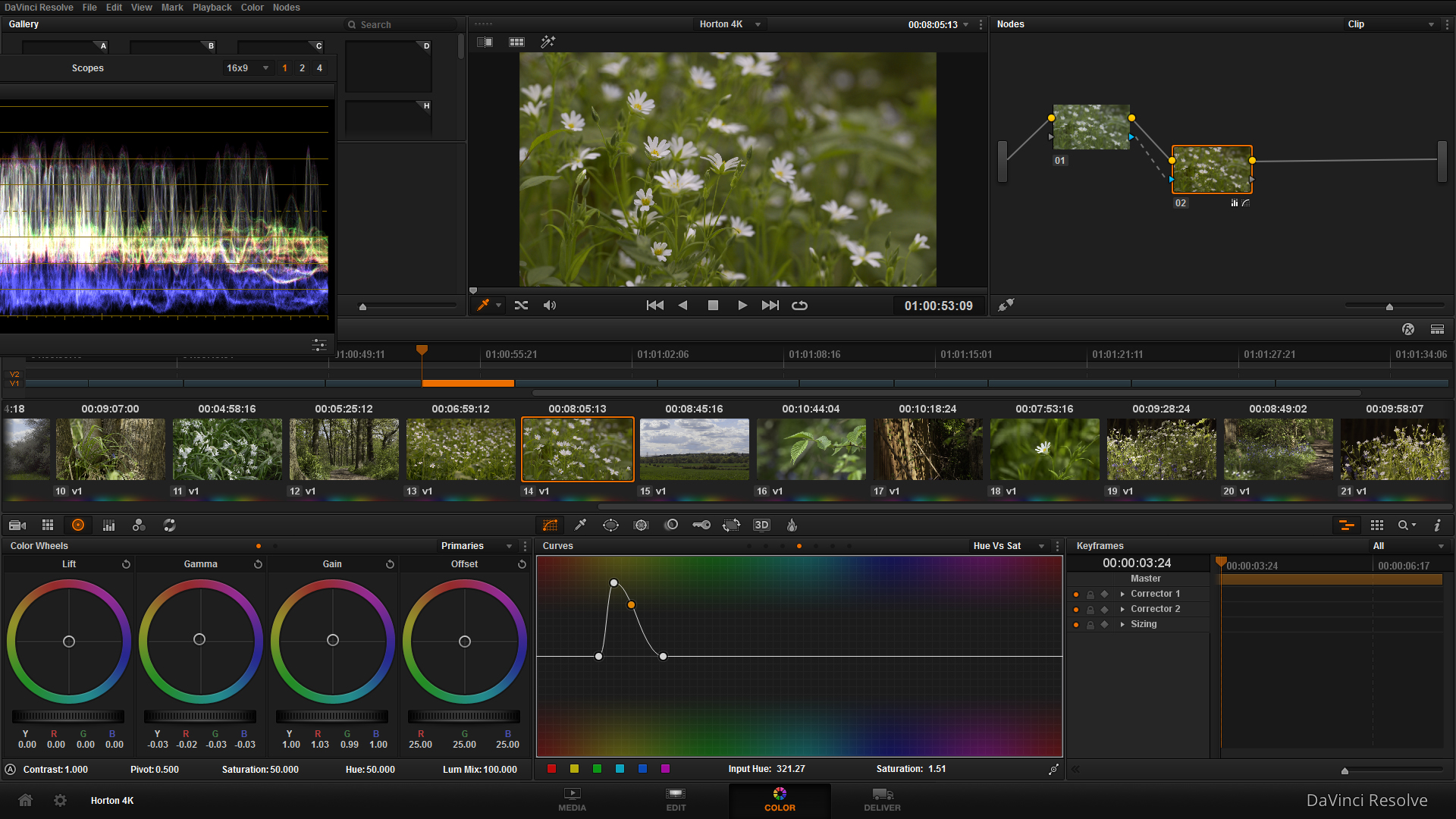
What does a picture profile do? Much like LUTS, picture styles adjust the intensity level of the; Sharpness, Contrast, Saturation and Colour Tone in the image, so what picture profile you use can change the 'look' of the video you capture.
Check out this video I put together today showing the results of the cameras picture profiles, and others I have loaded onto the camera. You can see a clear change in the image, but it is subtle differences that will make your video work stand out.
https://vimeo.com/85655816
I previously used the Neutral picture profile, customized to reduce the contrast, saturation and colour tone to produce a very grey and flat image. I was using this profile to achieve this look, as it is how RAW footage is captured to then be graded in post production. Neutral does replicate this 'flat' look, but after doing research into other profiles, Neutral reduces the data that is required in the picture (the contrast and saturation) that I would then put back in in post. This causes noise to be generated in the image, and can cause it to look unnatural and crushed, as the contrast and saturation that had been removed by the picture profile is being added back in later in the workflow.
That was long, but I hope it makes sense. If you compare the 'Standard' to 'Neutral' there is an evident drop in saturation and contrast, with a loss of detail in the top of the trees. If you compare 'Neutral' to 'VisionColor', there is an increase in saturation and contrast in the shadows and highlights.
The 'Neutral' picture style, similar to Technicolor CineStyle reduces the data the sensor captures, so I would not recommend using it if you plan to do colour correction and grading in your workflow. REMEMBER - whatever you capture when out filming will 'burn in' the detail, colours, sharpness and contrast into the image, making it harder to edit and remove unwanted errors. So, it would be better to use a profile that holds the data and detail so if wanted, you could work on grading the footage later.
From tests and experimenting, I favor the VisionColor profile; it is not as destructive as Neutral, holding colour and contrast without making the image flat. I definitely recommend checking them out here.
Next Question from SAHIB on Twitter: "Can ND filters change the style of video?"
Answer: This does depend on what and where your video shoot is. If you are working indoors, or with lighting that can be controlled by you then neutral density filters may not be required as you can alter the brightness of the scene by reducing the intensity of the lights. However, if you're out filming in a situation where you have little to no control over the lighting, then ND filters are key.
Personally I use variable ND filters, currently from Polaroid but much better filters are available from Hoya & Tiffen. The function of these filters is to reduce the light entering the lens, meaning camera settings can be kept the same. This allows you to follow the 180 degree shutter rule, which means keeping your electronic shutter speed at 1/50th to reproduce film-like and realistic motion blur.
So, with your shutter speed locked at 1/50, and your chosen aperture has been set, the only other exposure altering options you have is to ride the camera ISO to make the image brighter or darker.
PROBLEM!
With a fast aperture of F/2.8, and you are currently shooting in sunny daylight, your image is going to be very over exposed. Reducing the aperture to F/8 or F/11 may correctly expose the image but you have lost your depth of field! What to do!
Get some Variable ND Filters!
These ND filters rotate, allowing a variable ND amount to be set externally, without changing your cameras settings! This means that you can keep your cinematic depth of field and realistic motion blur without reducing the shutter speed to 1/250th or your aperture to F/11.
I recently shot this video using an ND filter on an 85mm T/1.5, which allowed me to shoot continually at T/1.5 for extreme shallow depth of field.
Making a quick edit: Variable ND filters are one of many options. ND Filters also come in stops; increasing by a factor of doubling so 2, 4, 8 etc. If you can stretch to separate stop ND filters they work just as well, and with the lower end (under £100 products) they will be better quality than one under £100.
In videography and cinematography, ND filters are applied in the matte box in front of the lens. So if you plan to use one, look in to matte boxes with the ability to add filters, but prepare to pay for it!
http://vimeo.com/84790518
Well, that covers Video Questions for today! I hope to have answered and covered all bases, and remember they are from my personal knowledge and experience.
Got any more? Send them my way!